Virtualization is a fairly old technology but it is still very relevant for cloud computing.
What is Virtualization?
 |
|---|
| https://resources.infosecinstitute.com/topic/11-points-consider-virtualizing-security/ |
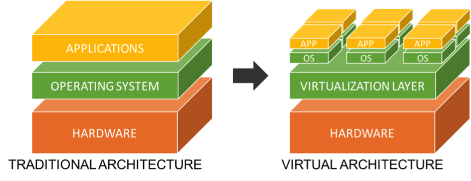
Virtualization refers to the technologies that allow a single physical computer environment to operate as multiple virtual machines at the same time, by transforming the physical hardware resources of a computer into virtual hardware resources.
What is a Hypervisor?
The virtualization software is called a hypervisor. It plays a key role in managing the virtualized environment.
Hypervisor is the software that creates and manages VMs to allow multiple operating systems to run on a host computer at the same time.
What does the Hypervisor do?
- The hypervisor shares the physical hardware resources among the VMs such that each guest OS appears to have its own hardware resources including CPU, memory, storage and network adapter.
- As a result of the abstraction provided by the hypervisor, the guest operating systems are no longer bound to the underlying physical hardware.
- The hypervisor also ensures that the guest operating systems do not interfere with each other.
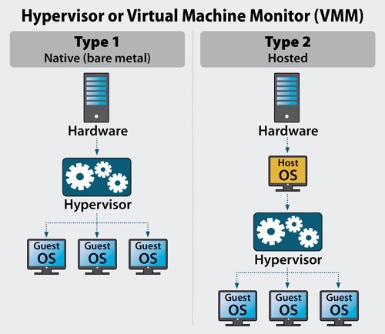
What are the types of Hypervisors?
There are 2 types of hypervisors - Type1 or Bare metal hypervisor and Type2 or Hosted hypervisor.
 |
|---|
| https://www.serverwatch.com/virtualization/hypervisor-server/ |
The differences between the two are listed below.
| Type1 Hypervisor | Type2 Hypervisor | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | It directly sits on the physical server and has direct access to the physical hardware. | It sits on top of a host OS and so it does not have direct access to the physical hardware. It runs as a software application on the host OS. |
| 2. | It is ideal for virtualization of physical servers | It is ideal for client computers, i.e, desktops and laptops. |
| 3. | Example are VMware ESXi and Microsoft Hyper-v. | Example is VMware player, VMware workstation and Microsoft virtual server. |
| 4. | It is controlled by the admin from hypervisor mgmt software installed in a desktop/laptop. For example, vSphere Client is a Windows program which can be used to configure the ESXi host and manage VMs. | It can be managed directly from the UI of the client computer. |
What is a Virtual Machine (VM)?
A VM is a software implementation of a physical computer. It is also referred to as a guest machine.
VMs run like physical computers. They have an operating system and applications, and they’re completely independent of one another. Multiple VMs can run on a hypervisor. The hypervisor manages the resources that are allocated to these virtual environments from the physical server. Since they are independent, different operating systems can be run on different virtual machines. They are also extremely portable. A virtual machine can be moved from one hypervisor to another hypervisor on a completely different machine almost instantaneously.
What are the benefits of Virtualization?
Virtualization and VMs are at the center of cloud computing and provide many benefits.
- Cost Savings - Running multiple VMs from a single physical infrastructure leads to server consolidation which results in savings in infrastructure, maintenance, electricity, etc.
- Speed and Agility - VMs can be spun off relatively easily and quickly as compared to provisioning a new environment in the traditional architecture.
- High availability - If a host goes down, the VMs can be moved to another hypervisor on a host that is working, leading to the high availability of these machines. This also helps with disaster recovery.
Please follow this link for the beginner’s guide to Cloud Computing.
Reference: Introduction to Cloud Computing