What is Cloud Computing?
Cloud Computing is the delivery of on-demand computing resources, from applications to data centers, over the internet on a pay-for-use basis. Examples of computing resources include networks, servers, storage, applications and services.
The cloud service market is predicted to grow drastically in the coming years. Some of the cloud service providers are Amazon Web Services (AWS), Google Cloud Platform (GCP), IBM Cloud, Microsoft Azure, Oracle Cloud, Salesforce, SAP, etc.
What are the benefits of Cloud Computing?
The Cloud provides globally distributed, scalable and cost-effective computing resources.
- High reliability from having globally distributed resources.
- Faster time to market as resources are elastically provisioned and released based on the demand, giving organizations the ability to quickly respond to demand.
- Cost-effective from resource pooling and the pay-as-you-go utility model. This also helps reduce upfront infrastructure costs.
- Cloud provides access to innovative technologies such as IoT, AI, blockchain and predictive analytics.
What are the challenges with Cloud Computing?
Most of the challenges are based on perceived risks with security and data protection.
- Data ownership and data safety - Security is an important consideration when you’re allowing a third-party to maintain business-critical data.
- Dependency on a third party for infrastructure availability and performance.
- Saas application access relies on having a good internet connection.
As a customer, what are the various options I have?
There are 3 deployment models and 3 service models for the cloud.
The 3 Deployment Models are:
 |
|---|
| The 3 Deployment Models (https://www.dotnettricks.com/learn/azure/understanding-cloud-computing-and-microsoft-azure) |
- Public Cloud - when the cloud infrastructure is shared by multiple companies, for example using the multi-tenant architecture.
- Private Cloud - when the cloud infrastructure is provisioned for exclusive use by a single organization. It could be on-premise or over the cloud.
- Hybrid Cloud - a mix of both public and private clouds. For example, a business could have business-critical applications running on a private cloud and the rest on a public cloud.
The 3 Service Models are:
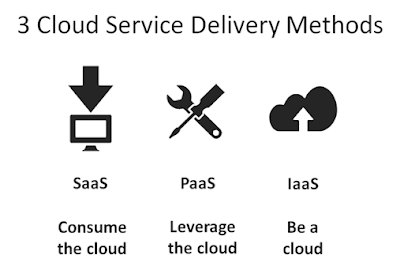 |
|---|
| The 3 Service Models (http://cloudcomputing124.blogspot.com/2013/01/understanding-cloud-computing-3-service.html#.X3WtPC1h01I) |
| Service Model | Vendor Control | Customer Control |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Iaas | Infrastructure, Servers, Storage, Networking | OS, Platform, Application |
| 2. Paas | All of the above + OS + Platform | Application |
| 3. Saas | All of the above + Application | None |
Let’s use the metaphor of a car to better understand the 3 service models.
 |
|---|
| Leasing a car = Iaas; Renting a car = Paas; Hiring a taxi = Saas |
Leasing a car = Iaas
Leasing a car is similar to the experience of using Iaas. While leasing a car, you are particular about the model/make of the car, the performance, the colour, etc. You are the one driving the car and also paying for the fuel and tolls you encounter.
Renting a car = Paas
Renting a car is similar to the experience of using Paas. You are not particular about the model/make of the car, the performance, the colour, etc. You are the one driving the car and also paying for the fuel and tolls.
Hiring a taxi = Saas
Hiring a taxi is similar to the experience of using Saas. You are not particular about the model/make of the car, the performance, the colour, etc. You are not the one driving the car and also not paying for the fuel and tolls, as this is baked into the price.
Please follow this link to explore how the Cloud supports and enables emerging technologies.
Reference: Introduction to Cloud Computing