In this series, we would be exploring, at a high level, some ideas, techniques, and algorithms that are at the foundation of AI. AI covers a wide range of techniques and in this series, I would be covering the following categories of problems:
- Search – searching for a solution to a problem, for example driving directions from point A to point B
- Knowledge – making inferences given some information
- Uncertainty – dealing with uncertain events
- Optimization – locating the best option among a possible set of solutions
- Learning – being able to perform a task by learning from data
- Neural Networks – drawing inspiration from human intelligence
- Language – understanding natural language
In this post, we will explore Language.
7. Natural Language Processing
So far, the AI problem areas we dealt with needed us to formulate the problem in a way AI can understand. Now we will look at some ideas that will enable AI to interpret our language.
Natural Language Processing (NLP) is about coming up with algorithms that will enable AI to process and understand natural language. It involves understanding the syntax and semantics of the human language to generate sentences, to make predictions about texts in a written or spoken language and to do much more.
Applications
Some of the tasks under NLP are as follows:
- Automatic Summarization - summarizing the contents in a document.
- Information Extraction - identifying key information from a given document.
- Language Identification - identifying the language on a page. For example, the experience of a web browser recognizing that the webpage you have opened is in another language and asking if it needs to be translated into English.
- Machine Translation - translating text from one language to another.
- Named Entity Recognition - identifying names of entities such as companies, people, location, etc. which are usually the relevant parts of a document.
- Speech Recognition - processing and interpreting audio as done by Siri, Amazon Echo or Alexa.
- Text classification - grouping text into categories. For example, categorizing an email as a Spam email or an Inbox item. Another example would be sentiment analysis wherein a product review is categorized a positive or negative.
- Word Sense Disambiguation - determining the meaning of a word depending on the context in which it is used.
- Information Retrieval - finding relevant documents in response to a user query
- Topic Modeling - discovering the topics for a set of documents; topics such as the imp people, objects, etc. or any imp words or keywords that set that doc apart from others.
Approach
Understanding the structure and semantics of a language are the two main challenges in the world of NLP.
Understanding the structure of a language
We need a way to tell the AI which English structures are valid and which are not. Context-free grammer is a way to describe the syntactic structure of natural languages. Using this method we can split a sentence into different parts and construct syntax trees.
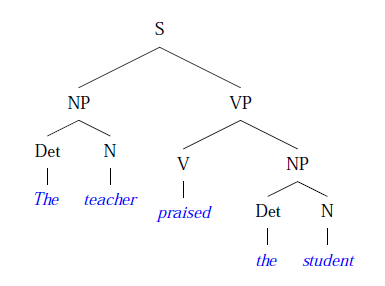 |
|---|
| Using Context-free grammer to build a syntax tree (https://www.pling.org.uk/cs/com6791.html) |
Context-free grammar rule enables AI to learn the structure of language and generate syntactically correct sentences.
Predicting the most likely word
Take the example of 2 sentences, “I ate a banana” and “I ate a building”. They are both syntactically correct sentences. We need a way to tell the AI that the second sentence is not likely to be true.
n-gram is a concept where we can feed the AI with a huge corpus of data and let the AI learn the most likely sequence of words - sequence of 2 words (bigram), 3 words (trigrams), etc.
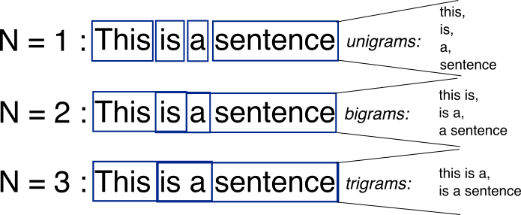 |
|---|
| Splitting a sentence into uni-, bi- and trigrams (https://web.archive.org/web/20180427050745/http://recognize-speech.com/language-model/n-gram-model/comparison) |
Word tokenization enables the AI to split a sequence of characters into words. Applying n-gram, word tokenization and Markov’s model, AI can predict the most likely word, for example, the 3rd word given a sequence of 2 words.
Classifying text
For identifying an email as spam or categorizing a product review as positive or negative, AI analyzes the words in the text.
Bag-of-words model represents text as an unordered collection of words. The idea is that the words in the text are what is important, the syntax or structure of the sentence being irrelevant.
Naive Bayes is a popular method used to categorize text. Naive Bayes, along with the Bag-of-words model, can predict the probability of a sentiment being positive or negative.
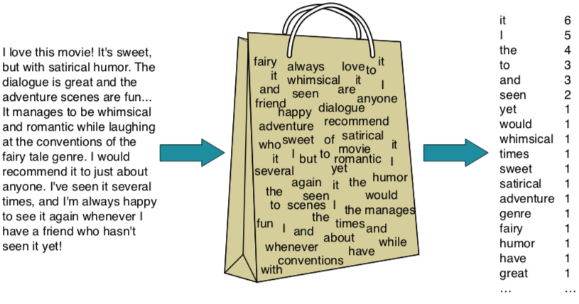 |
|---|
| Represent a movie review as a bag-of-words - the order of words is ignored; only the frequency is considered (https://web.stanford.edu/~jurafsky/slp3/4.pdf) |
Given enough training data, we can train the AI to be able to look at natural language, figure out which words are likely to show up in positive as opposed to negative sentiment messages and categorize them accordingly.
Identifying unique words in a document
AI extracts the unique words in a document by looking for words that appear most often because they are likely the important words. This makes Topic Modeling, mentioned above, possible.
Term frequency (TF) is the number of times a term appears in a document. AI considers only the content words and ignores the function words. Function words are words that have little meaning on their own but are used to grammatically connect other words. Examples are the, a, is, of, etc. This is in contrast to content words, which carry meaning.
Inverse document frequency (IDF) is the measure of how common or rare a word is across documents. AI arrives at the ranking of important words in a document by multiplying TF by IDF, also known as tf-idf. This helps AI identify imp words or keywords that set the doc apart from others.
Understanding the semantics
AI understands the meaning of words by finding the relationship of all words in the dictionary with each other. WordNet is a dataset that has definitions of words and information on how they relate to each other.
In the world of NLP, words are represented as vectors (Word representation). Words with similar meaning will have similar vector representations. word2vec is a model for generating word vectors. It uses skip-gram architecture, which is a neural network architecture for predicting context words given a target word.
The distance between words is the difference between their vectors. The distance is closer to 0 if the meanings are similar and closer to 1, if otherwise.
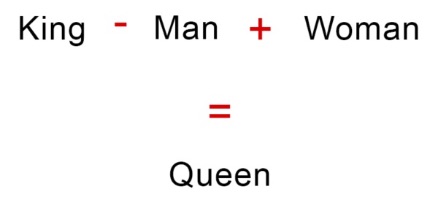 |
|---|
| Power of vectors (https://searchengineland.com/word-vectors-implication-seo-258599) |
Using vectors, AI can generate words by extracting the relationship between 2 words and applying that relationship to a 3rd word. A famous example is king - man + woman = queen. Here, the AI calculates what got “man” to “king” and applies it to “woman”, to arrive at “queen”.
Reference: CS50’s Introduction to Artificial Intelligence with Python